Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you suspect a serious injury or infection, seek immediate medical attention from a qualified healthcare provider.
Severe Finger Trauma: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
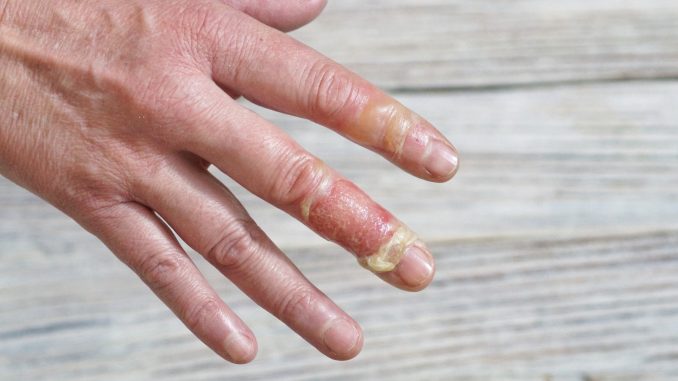
Hand injuries are among the most common types of trauma seen in emergency rooms, but some cases are more severe and require urgent medical intervention. The image above shows a case of severe finger trauma, with exposed tissue, swelling, and possible infection — a situation that demands immediate attention.
Understanding what causes such injuries, how they are treated, and what steps can be taken to prevent them is essential for both patients and caregivers.

Common Causes of Severe Finger Injuries
Finger trauma can happen in many ways, ranging from accidents at home to workplace hazards. Some of the most frequent causes include:
-
Crush injuries: Fingers can get caught in machinery, car doors, or heavy equipment, leading to tissue damage, fractures, and skin loss.
-
Industrial accidents: Jobs involving power tools, saws, or presses are high-risk for partial amputations and deep lacerations.
-
Burns and frostbite: Severe thermal injuries can cause necrosis (death of tissue) and require surgical debridement.
-
Animal or human bites: These can lead to infection and extensive soft tissue damage if not treated promptly.
-
Infections following minor cuts: A small untreated wound can progress to cellulitis, abscess formation, or necrotizing fasciitis in extreme cases.
Medical literature, including studies published in the Journal of Hand Surgery, confirms that crush injuries and high-pressure accidents are the leading causes of complex finger trauma worldwide.

Recognizing Serious Hand Trauma
Not all injuries are immediately obvious in severity. Warning signs that indicate urgent medical attention is needed include:
-
Severe swelling and discoloration
-
Visible bone, tendon, or muscle
-
Loss of sensation or movement in the finger
-
Persistent bleeding that does not stop with pressure
-
Signs of infection such as pus, fever, or spreading redness
Prompt recognition and treatment are critical. Delays in care can result in permanent loss of function or even the need for amputation.

Emergency Treatment and Hospital Care
When a patient presents with such a severe injury, doctors follow a structured approach:
-
Stabilization: Stopping bleeding, cleaning the wound, and providing pain relief.
-
Imaging: X-rays are performed to assess fractures or foreign bodies.
-
Debridement: Removal of dead or infected tissue to prevent the spread of infection.
-
Antibiotics: Intravenous antibiotics are started immediately if there are signs of infection.
-
Surgical Repair: Depending on the damage, reconstructive surgery or skin grafting may be necessary.
In severe cases, microsurgery is used to repair blood vessels and nerves, improving the chances of saving the finger.

Possible Complications
If left untreated or if infection spreads, complications may include:
-
Sepsis: A potentially life-threatening infection of the bloodstream.
-
Chronic pain or stiffness: Resulting from scar tissue or nerve damage.
-
Loss of function: Partial or complete loss of movement in the affected finger.
-
Amputation: In extreme cases, if tissue death cannot be reversed.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), early medical intervention significantly reduces the risk of complications and improves functional recovery.

Rehabilitation and Recovery
Recovery from severe finger trauma often involves weeks or months of rehabilitation. This may include:
-
Physical therapy: To restore range of motion and grip strength.
-
Occupational therapy: To relearn fine motor skills and adapt to any lasting limitations.
-
Wound care: Regular dressing changes and monitoring for signs of infection.
Patients are also encouraged to follow a balanced diet and maintain good overall health, as this supports faster healing.

Preventing Hand Injuries
Many hand injuries can be prevented through basic safety practices:
-
Use protective gloves when working with machinery or chemicals.
-
Follow workplace safety guidelines and ensure proper training.
-
Keep knives and tools sharp and in good condition to avoid slips.
-
Treat even small cuts promptly with cleaning and antiseptic to prevent infection.
Education and awareness are key to reducing the frequency and severity of traumatic hand injuries.
Conclusion
Severe finger trauma, such as the case shown above, is a medical emergency that requires quick action, professional treatment, and careful follow-up. Understanding the causes, recognizing danger signs, and taking preventive measures can help save not just fingers, but overall hand function and quality of life.
If you or someone you know suffers a serious hand injury, seek emergency medical care immediately. Early treatment is the most effective way to preserve mobility and prevent long-term complications.
Sources
-
American Society for Surgery of the Hand (ASSH): Hand Trauma and Treatment Guidelines
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Injury Prevention and Control
-
Journal of Hand Surgery – “Management of Severe Hand Trauma” (2023)